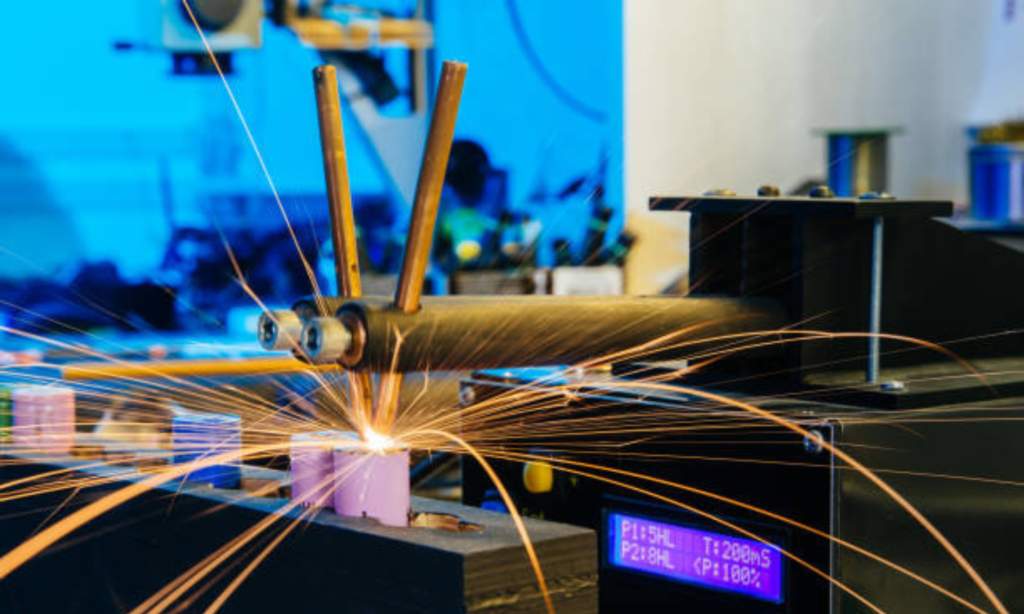
What is resistance welding? Resistance welding is a process that joins materials with heat and pressure. It does not require filler materials or fluxes.
This technique employs the heat generated from the electrical resistance of the material combined with the pressure applied to join the parts. This method is commonly utilized in automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications owing to its speed and efficiency. Resistance welding encompasses several types like spot welding, seam welding, and projection welding, each with specific uses based on the materials and desired strength of the joint.
The process is favored for its repeatability, low energy consumption, and ability to automate, making it a cost-effective solution for mass production settings. With advances in technology, resistance welding continues to evolve, offering high-quality, durable welds for a wide range of manufacturing needs.
Igniting The Basics Of Resistance Welding
The Principle Behind The Sparks
At its core, resistance welding works by fusing materials. It does so through a blend of heat, pressure, and time. As current flows through the resistance caused by the materials’ touchpoint, intense heat is generated. This heat, along with applied force, creates a solid weld in seconds.- Current: Flows through conductors.
- Resistance: Opposes the current, generating heat.
- Heat: Melds the materials.
- Pressure: Unifies the parts solidly.
Varieties Of Resistance Welding Techniques
Different resistance welding methods exist, catering to various industrial needs. Each has its utility, precision, and application, as outlined below:| Type | Use | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Spot Welding | Joining sheet metal | Single point welds |
| Seam Welding | Seals continuous seams | Rolling electrodes |
| Projection Welding | Works on embossed features | Multiple weld spots |
| Butt Welding | Joining rod or wire ends | Parallel electrodes |
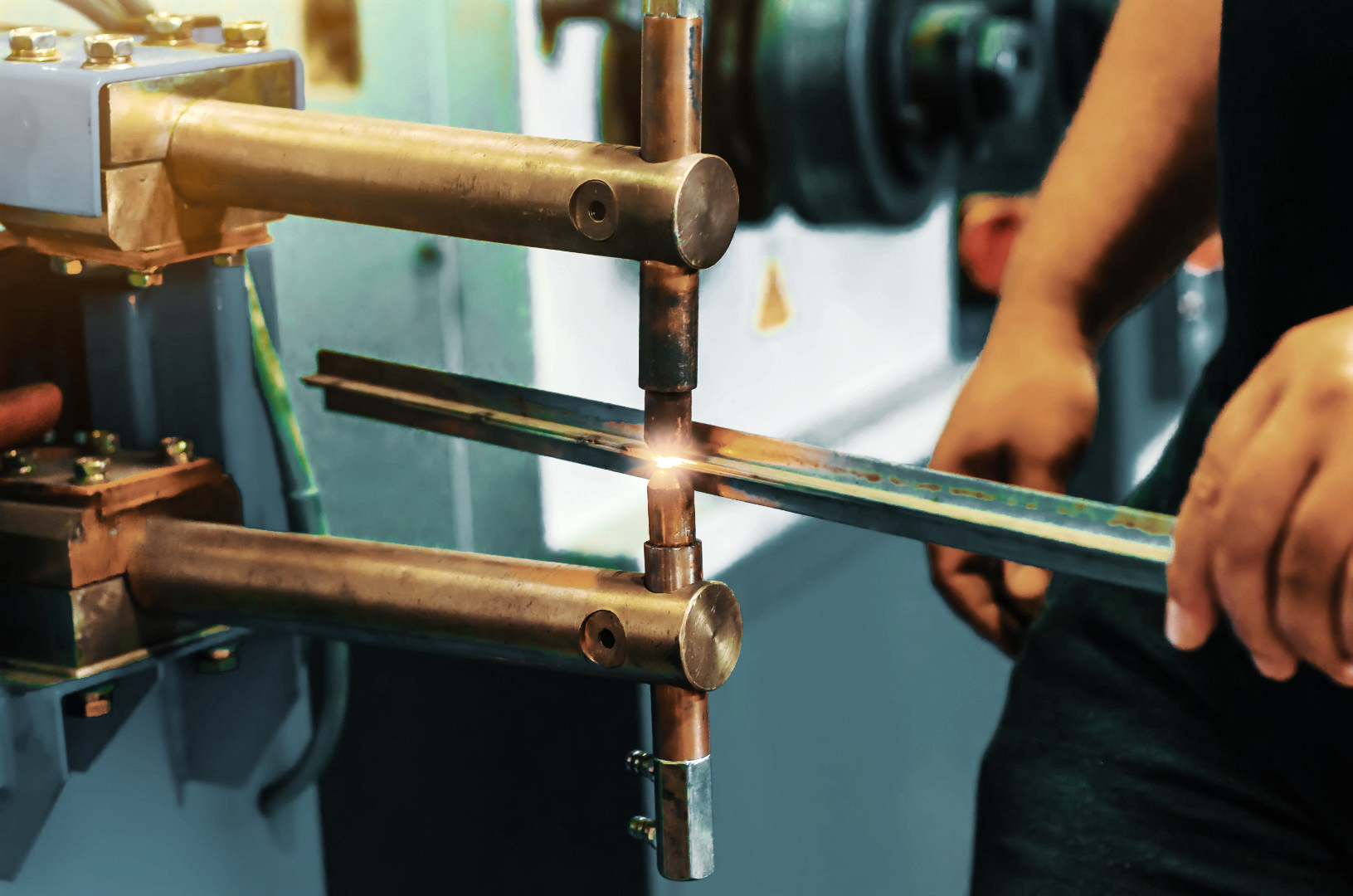
Credit: www.tuffaloy.com
The Anatomy Of A Resistance Weld
Key Components Of Welding Machines
Resistance welding machines have specific parts that work in harmony. Each plays a crucial role in the welding process.- Power Source: Supplies electricity.
- Control System: Manages the flow of power.
- Electrodes: Conduct current and apply pressure.
- Welding Force: Pushes the materials together.
Material Considerations
Selecting the right material is essential for a successful weld. Not all metals weld the same. Here are some factors to consider:| Material Property | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Conductivity | Affects the heat generation. |
| Thickness | Influences the current required. |
| Melting Point | Determines the energy needed. |
The Heat Is On: Understanding The Welding Process
Electrical Current’s Role
In resistance welding, electrical current is the star. Think of it as the welding glue. When current flows, it meets resistance. Resistance turns into heat. That heat gets so intense, it actually melts metal. Here’s a breakdown:- Intense Heat: Current’s flow creates it.
- Melting Point: Metals reach this from the heat.
- Solid Bond: Once cool, a super strong joint forms.
Pressure And Time: The Essential Parameters
Two heroes in resistance welding are pressure and time. They’re like a superhero duo for producing strong, reliable welds. First, pressure pushes the metal pieces together. It needs to be just right—not too soft, not too strong.| Pressure | Function |
|---|---|
| Consistent Application | Helps heat spread evenly. |
| Proper Force | Ensures metals fuse properly. |
- Too short: Weak joints.
- Too long: Overheated, brittle points.
- Just right: Perfect welds.
Strength Of The Bond: Quality And Testing
Evaluating Weld Integrity
Inspectors use a variety of tests to evaluate weld integrity. These ensure a weld’s reliability before it’s deployed in real-world applications. Tests include:- Tensile testing: Measures the force needed to pull the weld apart.
- Peel testing: Assesses the weld’s resistance when the metals are peeled away from each other.
- Microscopic examination: A detailed look at the weld under a microscope to identify any microscopic flaws.
Common Defects And Troubleshooting
Despite the precision of resistance welding, defects can occur. Recognizing and resolving these is key to peak performance. Some common defects include:| Defect Type | Description | Troubleshooting Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Expulsion | Material is ejected from the weld spot. | Adjust the pressure or heat settings. |
| Cold weld | Insufficient heat leads to a weak bond. | Increase the current or weld time. |
| Stick weld | Electrodes adhere to the material. | Clean or replace the electrodes. |
Resistance Welding In Action: Applications
Industry Sectors That Rely On Resistance Welding
Diverse fields depend on resistance welding for its efficiency and strength. This method’s adaptability makes it perfect for:- Automotive manufacturing: Car bodies need secure welds.
- Aerospace engineering: aircraft demand precise joins.
- Construction: Steel frameworks require robust bonding.
- Electronics: Circuit boards trust precision welding.
- Medical devices: Implants must have safe connections.
Innovations And Advancements
Resistance welding evolves constantly with technological advancements.| Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy-saving welders | Reduce operation costs |
| Programmable logic controllers | Enhance welding accuracy |
| 3D simulated welding | Improve training and safety |

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Safety First: Precautions And Protections
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Working with resistance welding equipment means exposure to high heat and sparks. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) becomes crucial. Here are some must-have PPE items for resistance welding:- Gloves: High-quality, insulated gloves protect hands from electrical shock and burns.
- Helmet with Face Shield: A helmet guards the head; a face shield protects the eyes and face from sparks and UV radiation.
- Protective Clothing: Flame-resistant aprons or jackets shield the body from sparks and heat.
- Safety Footwear: Sturdy boots prevent foot injuries and provide better grounding.
Best Practices In The Workshop
Following best practices can significantly reduce workplace accidents. Keep your workshop safe with these guidelines:- Regular Maintenance: Ensure equipment is well-maintained and inspected regularly.
- Clear Work Area: Keep the area clean and free of clutter to avoid accidents.
- Training: Train all staff thoroughly on equipment operation and safety protocols.
- Fire Safety: Equip the workshop with fire extinguishers and first-aid kits.

Credit: kartinausa.tv
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is Resistance Welding
What Is Meant By Resistance Welding?
Resistance welding is a process that joins metals using heat generated from electrical resistance to the current flow at the welding point.
Is tig welding resistance welding?
No, TIG welding is not a form of resistance welding; it is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode.
What Is the Difference Between Spot Welding and Resistance Welding?
Spot welding is a type of resistance welding where metal surfaces are joined at a single point. Resistance welding encompasses a wider range of techniques, including spot welding, that use electric resistance to generate heat for bonding metals.
What Is the Difference Between Resistance Welding and Arc Welding?
Resistance welding uses heat from electrical resistance to fuse materials together, while arc welding generates heat through an electrical arc between an electrode and the base material.
Conclusion
Resistance welding stands as an efficient, robust solution for fusing materials. It minimizes waste, optimizes production speed, and ensures durable joints. By understanding its principles and applications, industries can harness this technology for superior manufacturing outcomes. Embrace resistance welding for its precision and reliability in joining metal components.