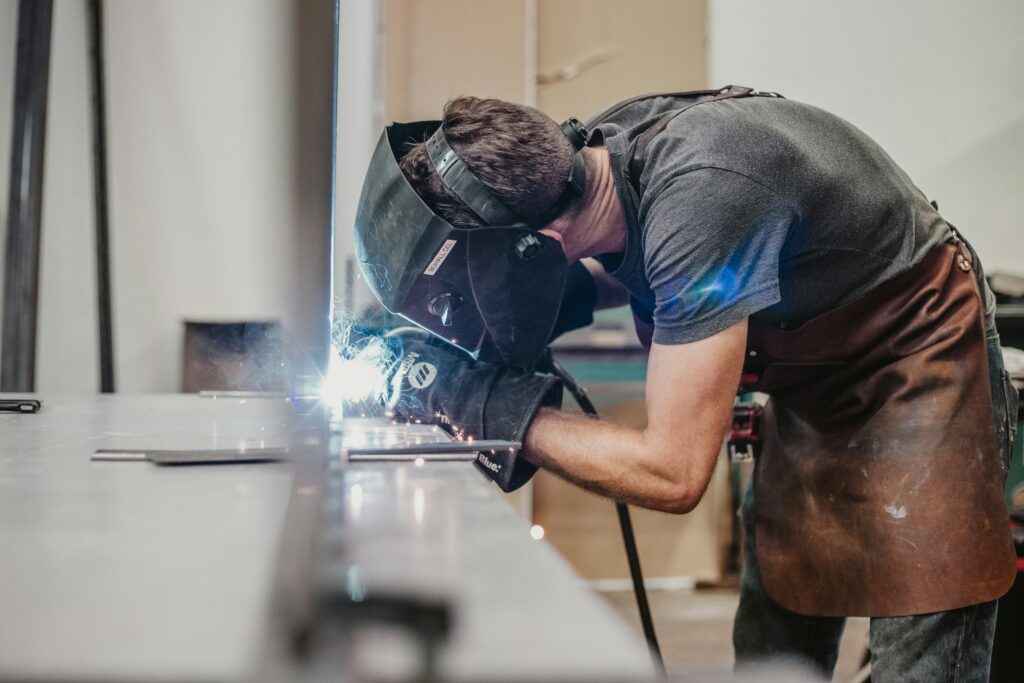
Arc welding is the process of joining metals using an electric arc. It employs a power supply to create an intense heat source.
Arc welding stands as one of the most prevalent methods of welding, utilized widely in industrial and construction settings due to its versatility and affordability. This process can join a variety of metals and alloys with commendable speed and strength.
Whether it involves repairing machinery, building structures, or crafting metal artwork, arc welding proves to be indispensable. It offers different techniques, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and gas metal arc welding (GMAW), each catering to specific materials and applications. Given its essential role in fabrication and repair, arc welding remains a fundamental skill sought after in the workforce and a subject of continuous advancement in welding technology.
Introducing Arc Welding
From Forge To Arc: The Evolution Of Welding
Welding’s history is rich with innovation. It dates back centuries. Blacksmiths once hammered heated metals to join them. The 19th century brought electric arc welding. This marked a significant turn in how we join metals. Modern welding offers precision and strength, shaped by years of advancement.- Forge welding involves hammering heated metals together.
- Gas welding involves using gas flames to melt metals.
- Arc Welding: Electricity creates a hot arc to fuse metal.
A Closer Look At The Arc Welding Process
Arc welding uses a power supply to create an electric arc between an electrode and the metal. This arc reaches temperatures hot enough to melt the metal. Once cooled, a strong joint forms. Different methods, like shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) or tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, offer unique benefits.| Type of Arc Welding | Common Use |
|---|---|
| SMAW (Stick) | Construction, Repair |
| TIG | Precision Work, Thin Metals |
Equipment Essentials: Gear That Sparks Creation
Power Sources And Electrodes: The Heart Of Arc Welding
At the core of arc welding lie two critical components: power sources and electrodes. Together, they create the intense heat needed to fuse metals. Understanding these elements is fundamental for every welder.- Power Sources: These come in various forms, with AC and DC generators being common. They power the welding arc.
- Electrodes: Chosen based on metal type, they conduct the current to create the arc.
| Power Source Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| AC Generator | Stable and cost-effective for thin materials |
| DC Generator | Better control for thick materials |
Personal Protective Equipment: Safety First
While the thrill of creation is exhilarating, safety never takes the back seat in arc welding. Personal protective equipment is not just essential; it is mandatory for every welder.- Welding Helmet: Shields the eyes and face from sparks and harmful light.
- Gloves: Protect the hands from heat, metal splatter, and electric shock.
- Apron or Jacket: Defends against sparks, providing body coverage.
- Boots: Prevent injuries from falling objects and enhance grip on slippery surfaces.
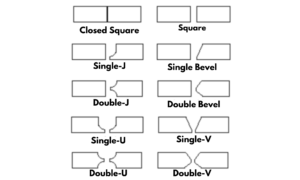
Types Of Arc Welding Techniques
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (smaw)
Commonly known as stick welding, this technique is widely used across the globe. It’s adaptable and straightforward, making it a favorite for outdoor use and construction sites.- Uses an electrode stick that arcs with the base metal.
- Create a weld pool to join two pieces of metal.
- Slag covering protects the weld from contaminants.

Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (gtaw/tig)
GTAW, or TIG welding, is noted for its pristine weld quality. It’s often used when precise, clean welds are essential, such as in aerospace or artistic applications.- Employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode.
- Shielding gas, like argon, protects the welding area from environmental factors.
- It works well with thin or high-alloy metals.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (gmaw/mig)
Also referred to as MIG welding, GMAW is popular for its speed and ease of use. This method is a go-to for both industrial fabrication and DIY projects.- Features a wire feeding system as the electrode.
- Continuous wire feed ensures long welds without interruption.
- Shielding gas, typically a mix of argon and carbon dioxide, guards against impurities.
Exploring Applications And Industries
Construction And Infrastructure Marvels
Arc welding creates structures that touch the skies. It is the backbone of modern infrastructure. Welders use this method to assemble frameworks for buildings and bridges. This ensures safety and durability over time. Some outstanding examples include:- Steel columns and beams for high-rise buildings
- Secure joints in bridges and overpasses
- Reinforcement in tunnels and stadiums
Automotive And Aerospace Mastery
Arc welding boosts the production of vehicles and aircraft. Advanced techniques allow for strong, lightweight designs. This benefits fuel efficiency and safety. Key applications in these industries include:| Automotive | Aerospace |
|---|---|
| Chassis assembly | Airframe components |
| Exhaust systems | Turbine engines |
| Body panel joining | Space structures |
Artistic Expressions In Metalwork
Metal becomes a canvas with arc welding. Artists craft intricate sculptures and decorative pieces. They transform metal into expressive art. Unique creations range from garden statues to complex installations in public spaces. Highlights include:- Outdoor metal sculptures
- Architectural accents
- Custom furniture
Challenges And Advancements In Arc Welding
Combating Common Arc Welding Difficulties
Arc welding demands skill and precision. Operators encounter several challenges:- Weld consistency: Achieving uniform welds requires steady hands and concentration.
- Safety risks: Electric shocks and exposure to fumes pose health threats.
- Equipment wear: Frequent use leads to degradation of welding tools.
- Training: Comprehensive programs improve operator skill levels.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): This shields workers from potential hazards.
- Maintenance: Regular upkeep of equipment ensures functionality and longevity.
Technological Innovations Shaping The Future
Technological advancements are aiding arc welders in numerous ways. Here are some innovations:| Advancement | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automated welding systems | Boost precision and speed while reducing labor intensity. |
| AI-driven quality control | Automatically detects and rectifies weld defects. |
| Welding simulators | Offer trainees risk-free, hands-on experience. |
Learning The Craft: Training And Certification
Navigating The Path To Professional Welding
To become a skilled welder, begin with basic training programs. These are offered at vocational schools and community colleges. Focused courses teach the fundamentals of arc welding. They cover metal properties, welding techniques, and safety measures.- Introduction to welding concepts
- Hands-on practice in various welding processes
- Understanding welding safety protocols
Certification Bodies And Standards
Certifying bodies set benchmarks for welder qualification. They ensure welders meet essential industry standards. Recognized organizations, like the American Welding Society (AWS), offer various certifications tailored to different welding processes and positions.| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| Certified Welder (CW) | Tests skills in specific welding processes |
| Certified Welding Inspector (CWI) | Validates expertise in welding inspection and quality control |
| Certified Welding Educator (CWE) | Aims at professionals teaching the art of welding |
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Arc Welding
What Do You Mean By Arc Welding?
Arc welding is a process that joins metals using an electrical arc to melt the workpieces and a welding rod.
What Is The Difference Between Arc And Mig Welding?
Arc welding uses an electric arc to melt metals, while MIG welding feeds a wire electrode to create the weld. Arc welding is versatile for various materials; MIG is faster and easier for thin metals.
Is Arc And Stick Welding The Same?
Arc welding and stick welding refer to the same process, involving an electric arc to fuse metals using a consumable stick electrode.
What Is Arc Welding Best For?
Arc welding excels at joining metals, especially steel and iron, for industrial fabrication and construction due to its durable, strong welds and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored, arc welding stands as a pivotal technique within the fabrication industry. Its versatility and strength ensure it remains a top choice for professionals. Embracing the nuances of arc welding promises enhanced quality and efficiency in metalwork projects.
Mastering this skill opens a world of robust, durable construction possibilities. Choose arc welding to unlock the full potential of your metal creations.