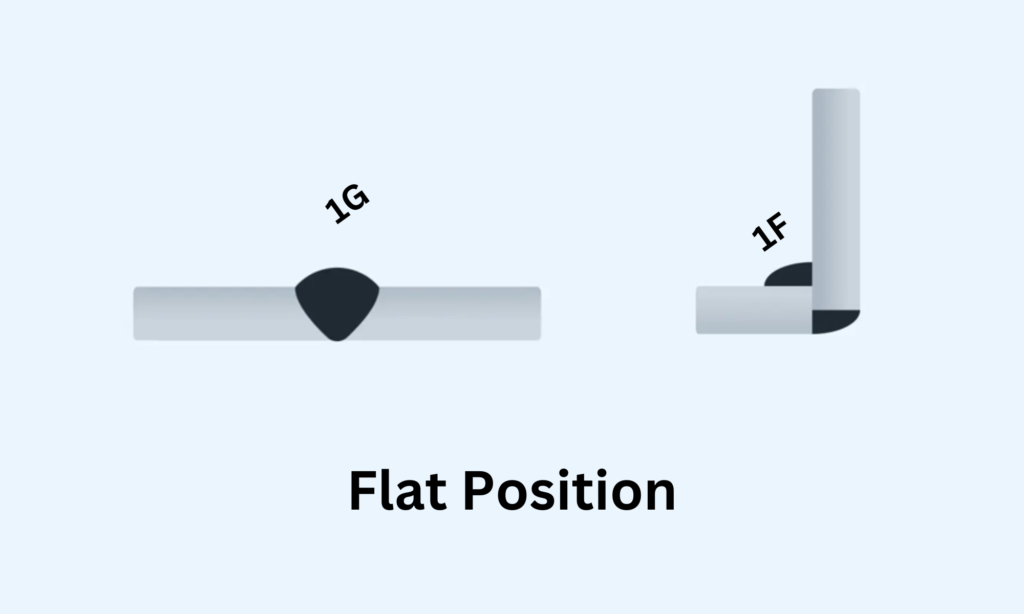
Weld position 1G refers to flat welding. It is the position used for groove and fillet welds where the welded joint lies in a horizontal plane.
Understanding weld positions is crucial for both novices and professionals in the welding industry. The 1G position is often one of the first positions welders learn, as it allows for the easiest manipulation of the welding tool or electrode. It provides a stable environment for practicing bead appearance, weld penetration, and establishing a good welding technique with gravity on the welder’s side.
This position is also a common test position for certification because it serves as a fundamental skill in a welder’s repertoire. Choosing the right weld position impacts the quality and strength of the weld, and therefore, knowledge of the 1G position is pivotal for ensuring structural integrity and safety in welded projects.
The Basics Of 1g Weld Position
Defining The 1g Weld Position
The 1G position, also known as the flat position, refers to welding on the top side of the joint where the weld face lies horizontal. Welders use this position to join two pieces of metal effectively and smoothly. The gravity in this position helps deposit the weld bead evenly, making it a preferred choice for many jobs.- Orientation: Horizontal welding surface
- Axis: Horizontal weld axis
- Method: Bead runs flat
When To Use 1g In Welding Projects
1G welding is optimal for various applications. Its simplicity and ease of use make it the preferred position in multiple scenarios.| Applications | Reasons for Use |
|---|---|
| Pipe welding | Standard position for beginner-level pipe welding |
| Plate welding | Suitable for large, flat plates that can be easily manipulated |
| Sheet metal work | Ensures clean, flat seams for aesthetics |
Preparing For Horizontal Welding
Setting Up The Work Space
Begin with a clean and organized workspace. It’s vital for successful 1G horizontal welds.- Remove clutter and potential hazards.
- Ensure proper ventilation to avoid fume buildup.
- Have a stable work surface at the right height.
- Position fire extinguishers nearby for emergencies.
Selecting The Right Equipment
Choosing appropriate equipment is crucial for effective 1G welding.| Equipment | Importance |
|---|---|
| Welding Machine | Matches material and thickness. |
| Welding Rods | Correct size and material type. |
| Welding Helmet | Protects eyes and face. |
| Gloves and Apron | Shields against sparks and heat. |
Techniques For Mastering 1g Welding
Understanding The Horizontal Technique
The 1G welding position is also known as the horizontal technique. Here, the weld is performed on the upper side of a flat plate, resembling a table top. This position lays the foundation for more complex welds and requires the welder to perfect a smooth and steady travel speed. Proper body positioning is key to success in the horizontal technique—ensuring the weld pool is controlled accurately.Tips For Steady Hand Movement
Balanced and steady hand movement is crucial for delivering a quality 1G weld. Consider these tips:- Brace Your Hands: Use your free hand to steady your welding hand.
- Motion Practice: Without welding, practice the motion to build muscle memory.
- Joint Preparation: Ensure edges are clean and fit-up is proper before starting.
- Correct Angle: Hold the welding gun at a consistent 10-15 degree angle.
- Speed Control: Maintain a uniform speed that matches the melting rate of the metal.

Common Challenges In 1g Welding
Dealing With Gravity
In 1G welding, gravity can either be a friend or a foe. This position involves flat welding, where the welder operates on the top side of the joint. At first glance, it seems simple, but gravity can cause molten metal to sag or create an uneven weld bead. Ensuring stability in your hand movements helps control the flow of metal. The following points highlight key solutions to the gravity issue:- Secure the workpiece: It prevents any shifting that may occur during the welding process.
- Maintain a consistent speed: This ensures even distribution of the weld pool.
- Correct electrode angle: It directs the weld pool effectively and combats the forces of gravity.
Controlling Heat Input And Distortion
Too much heat can cause distortion, making the final product less accurate and aesthetically pleasing. In 1G welding, mastering the heat input is vital to maintaining structural integrity. Keeping the heat at an optimal level prevents warping and maintains the metal’s shape. Remember these guidelines to manage heat and distortion:- Preheat the metal: This can minimize the temperature difference and reduce overall distortion.
- Intermittent welding: Using a stitch-welding pattern allows the material to cool, thereby reducing the heat buildup.
- Post-weld heat treatment: This can relieve stresses in the material after welding and help in correcting any minor distortions.
Safety Measures During 1g Welding
Personal Protective Equipment
Welders must wear the right personal protective equipment (PPE). Protective gear shields against heat, sparks, and harmful light. Key items include:- Welding Helmet: Protects eyes and face from ultraviolet and infrared rays.
- Fire-Resistant Clothing: Prevents burns from sparks and spatter.
- Gloves: Insulated gloves guard the hands against electric shock and heat.
- Safety Glasses: Worn under the helmet for extra eye protection.
- Ear Protection: Muffles the noise and blocks sparks from entering ears.
- Boots: High-topped, steel-toed boots protect feet from falling objects and sparks.
Ventilation And Fume Extraction
Good ventilation is vital to clear hazardous fumes. Welding produces harmful gases that can affect health. Effective fume management includes:- Exhaust Hoods: These extract fumes at the source.
- Respirators: They provide clean air when ventilation isn’t enough.
- Regular Air Monitoring: Ensures fume levels stay safe.
Advancing Your Skills
Perfecting Weld Bead Appearance
A smooth, even weld bead is a sign of quality workmanship. To achieve that perfect weld bead appearance, consider these tips:- Maintain a consistent angle.
- Control your welding speed.
- Practice steady hand movements.
- Choose the right electrode.
Transitioning To More Complex Positions
Once you’ve mastered the 1G position, it’s time to take on new challenges.- Study the positions 2G, 3G, and 4G.
- Understand the complexities of each position.
- Build muscle memory through repetition.
- Seek feedback from experienced welders.
Frequently Asked Questions On Weld Position 1g
What Is The 1g Welding Position?
The 1G welding position is a flat position where the weld is horizontal and the axis of the weld lies flat. It is commonly used for plate welding and is considered one of the easiest positions to learn and execute efficiently due to its stability and accessibility.
How Does The 1g Position Affect Welding Quality?
Welding in the 1G position often results in high-quality welds due to the ease of accessing the weld joint and the stability the position provides. Gravity aids in achieving uniform bead appearance and penetration, which enhances overall weld quality when performed correctly.
Can 1g Welding Be Used For Pipe Joints?
No, the 1G welding position is not typically used for pipe joints. Instead, it’s designated for flat plate welding. For piping, positions are denoted differently, such as the 1G for a horizontal rolled pipe which is similar but specific to cylindrical shapes.
What Are The Advantages Of Using 1g Position?
The 1G welding position offers several advantages including ease of learning for beginners, greater welder comfort, and faster welding speeds. It also allows the use of gravity for better bead appearance and consistent penetration, ideal for large, flat surface projects.
Conclusion
Embracing the 1G welding position offers a solid foundation for beginners and experts alike. It’s essential for mastering the basics and achieving consistent, high-quality welds. Whether pursuing a career or tackling DIY projects, this horizontal technique is your gateway to welding proficiency.
Let your skills shine from here.